Welcome to the ultimate guide for embarking on a career in manufacturing. This sector, a critical engine of the global economy, embodies the innovative spirit of creating, building, and improving our world. Today, manufacturing stands at a crossroads where tradition meets technology, opening new doors for job seekers willing to adapt, learn, and grow.
Manufacturing revolves around people innovating for a greener planet, creating cutting-edge products, and keeping the industry running smoothly. Moreover, an industry values diversity, recognizing that unique perspectives and varied experiences drive creativity and success.
Whether you’re just starting or looking to make a career shift, this guide provides everything you need about manufacturing jobs, from educational requirements and areas of expertise to salary trends and the sector’s future outlook. Focusing on inclusive and diversity-focused companies, we aim to connect you with opportunities that match your skills and ambitions and embrace and celebrate your unique identity.
Let’s embark on this journey together, exploring the vast possibilities that manufacturing jobs offer. It’s a path to a fulfilling career where you can make a tangible impact on the world around you. Welcome to your manufacturing dream job guide.
Educational Requirements
To kick off a successful career in manufacturing, the right educational background plays a critical role. The diverse nature of manufacturing jobs means starting requirements can vary. Having a high school diploma might be enough for many entry-level roles. Yet, the industry is fast evolving, setting the bar higher for newcomers.
More and more, employers are in search of candidates who bring something extra to the table. This often means postsecondary education or specialized certifications. From two-year associate degrees focused on manufacturing technology to four-year bachelor’s degrees in biotech manufacturing jobs or manufacturing engineering jobs, the paths are as varied as the opportunities they open up.
Certifications matter, too. Earning industry-recognized credentials can significantly boost your job prospects. Certifications such as Certified Manufacturing Associate, Certified SOLIDWORKS Professional, or OSHA 30 Hour General Certification, to name a few, demonstrate your dedication and capability to potential employers.
Bottom line? Start your manufacturing education at any level; ascend with foundational knowledge, technical skills, and ongoing learning.
Areas of Expertise
The world of manufacturing jobs is vast, encompassing a wide range of specialties. As the sector continues to expand, so do the areas where professionals can shine. Here are some key expertise highly sought after in the industry:
- CNC Machining: With computer-numerical control (CNC) technology becoming more sophisticated, expertise in CNC machining is highly valued. It involves operating CNC machines to manufacture precision parts and components.
- Robotics: The integration of robotics into manufacturing lines is revolutionizing production processes. Specializing in robotics means working at the intersection of mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, and computer science to improve efficiency and innovation.
- Additive Manufacturing: Also known as 3D printing, additive manufacturing is changing how products are designed and produced, making it a cutting-edge field to specialize in.
- Manufacturing Engineering Technology: This area focuses on improving manufacturing processes, implementing design changes, and deploying new technologies on the production floor. Experts in manufacturing engineering jobs bridge the gap between engineering concepts and their practical application.
Whether your interest lies in the more traditional aspects of manufacturing or you’re driven by the allure of high-tech advancements, establishing yourself in one of these areas can set the stage for a fulfilling career.
Demographics in the United States
The landscape of manufacturing jobs in the U.S. is as diverse as the sector itself, with people of different ethnicities, genders, and ages contributing to the growth and innovation in the industry.
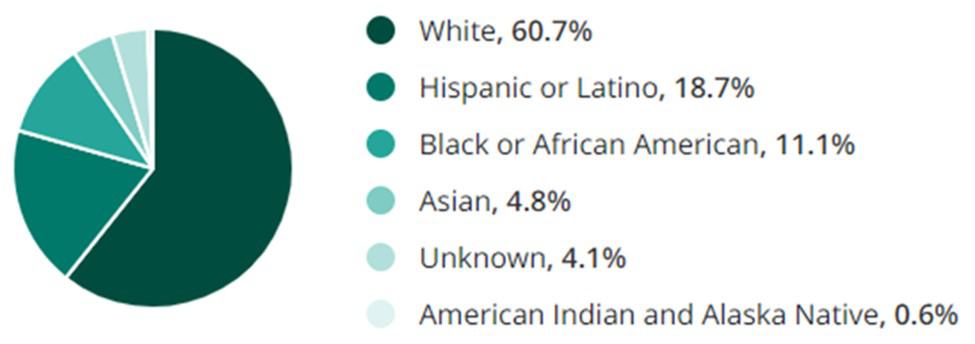
Ethnicity/Race:
Manufacturing is a melting pot of cultures and backgrounds, reflecting the global nature of the industry:
- White: 60.7%
- Hispanic or Latino: 18.7%
- Black or African American: 11.1%
- Asian: 4.8%
- Unknown: 4.1%
- Native American and Alaska Native: 0.6%
This diversity enriches the industry, bringing varied perspectives and ideas essential for innovation and problem-solving. This is essential not only for creativity but also for reflecting the diverse consumers the industry serves.
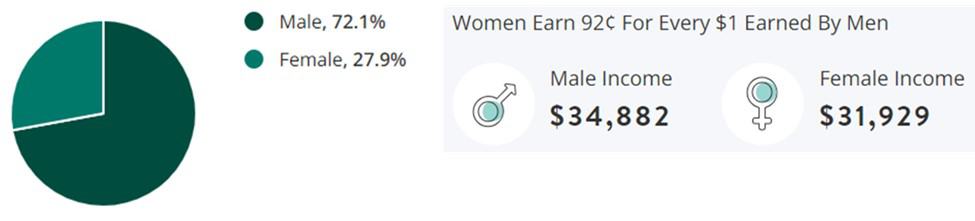
Gender:
Historically, manufacturing has been a male-dominated field, but the tide is changing:
- Male: 72.1%
- Female: 27.9%
This shift signals a growing recognition of the importance of gender diversity and women’s unique contributions to manufacturing.
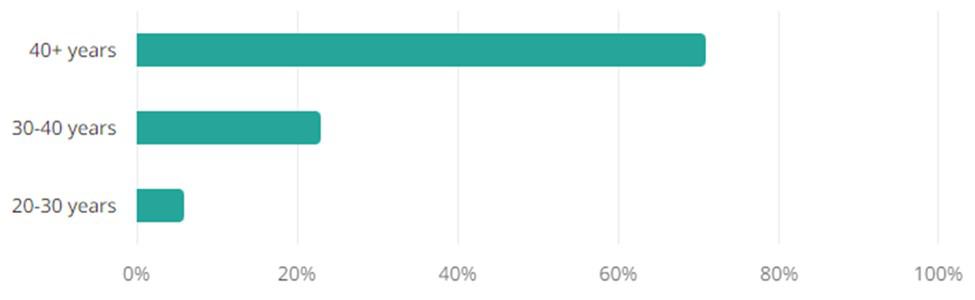
Age:
The age distribution within the manufacturing sector leans heavily to over 40 years old, showcasing the industry’s appeal to seasoned professionals. Manufacturing benefits from the experience and innovative thinking of experienced professionals. Attracting more young professionals, often more adaptable to new technologies and methods, is vital for driving the sector forward. At the same time, experienced individuals contribute a depth of knowledge and expertise in optimizing processes and maintaining quality standards.
Understanding these demographics highlights the importance of creating an inclusive environment that leverages the strengths of individuals from all walks of life. As the industry evolves, embracing diversity at all levels will sustain growth and foster innovation.
Salary Trends
The earning potential in manufacturing jobs varies, influenced by specialization, location, and years of experience. However, the sector generally offers competitive salaries reflecting the required skill and expertise.
- Entry-level positions often start around $40,000, providing a solid base for those new to the industry.
- Mid-career professionals, especially those with sought-after specializations in areas like additive manufacturing jobs can see salaries ranging from $60,000 to $80,000.
- At the higher end, experienced specialists and those in managerial or engineering roles, such as manufacturing supervisor jobs, can earn upwards of $120,000.
These salary trends underline the lucrative nature of manufacturing careers, rewarding technical proficiency and innovation. Professionals embracing Industry 4.0, robotics, and digital manufacturing through continuous learning can see their earnings grow with their expertise.
Hiring Trends
The demand for skilled professionals in manufacturing remains robust, driven by several key trends shaping the industry’s future. Here’s a closer look at what’s fueling the demand:
- Technological Advancements: The rise of Industry 4.0 technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and robotics are revolutionizing manufacturing processes. Companies seek individuals skilled in these areas to lead innovation and efficiency.
- Sustainability and Green Manufacturing: With an increasing focus on environmental sustainability, the industry needs professionals who can implement eco-friendly practices and sustainable production methods.
- Reshoring Efforts: A trend toward returning manufacturing jobs to the US from overseas creates new opportunities for domestic workers. This shift emphasizes the need for a skilled workforce ready to enter these roles.
- Skilled Trades Shortage: A notable gap exists in skilled trades such as machining, welding, and electrical engineering. This shortage presents an opportunity for new entrants to fill these essential roles.
The hiring trends indicate a strong and steady demand for manufacturing talent. Professionals updating skills, particularly in additive manufacturing and sustainability, will excel in the job market.
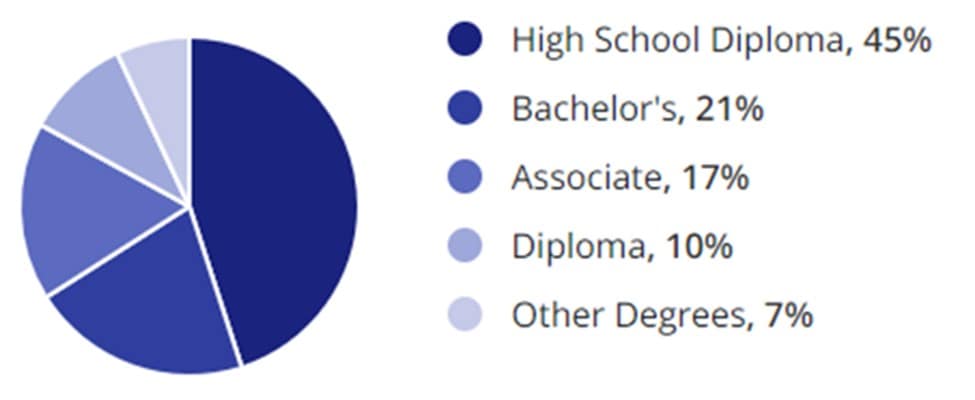
Education Levels
The manufacturing sector values varied educational backgrounds, reflecting the diversity of roles within the industry. The spectrum of education levels among professionals is broad, from technical certifications to advanced degrees.
- High School Diploma or GED: Many manufacturing roles start with the basics, requiring a high school education. Positions like assembly or essential machine operation often fall into this category.
- Technical Certifications: Certified Manufacturing Associate or OSHA 30 Hour General Certification provides specialized knowledge and skills directly applicable to the manufacturing floor.
- Associate’s Degree: Two-year degrees in fields like manufacturing technology or industrial engineering technology can open doors to roles with greater responsibility and higher pay.
- Bachelor’s Degree: A four-year degree in manufacturing engineering, mechanical engineering, or a related field is typically required for more advanced positions, including management and manufacturing engineering jobs.
- Master’s Degree or PhD: Higher education levels are often sought for research, development, and senior leadership roles. These positions focus on innovation and strategic direction within the manufacturing industry.
This educational diversity ensures that individuals at all stages of their academic journey can find a path into manufacturing. Moreover, the industry’s commitment to continuous learning and upskilling means educational advancement is encouraged and often supported.
Skills in Demand
Thriving in the dynamic world of manufacturing jobs requires a rich skillset that blends technical prowess with soft skills. The industry’s evolution, driven by technological advancements and a growing emphasis on sustainability, has highlighted several skills that are particularly in demand:
- Technical Proficiency: Understanding and operating advanced machinery, software, or production systems are fundamental. Proficiency in areas such as CNC machining, additive manufacturing, and robotics is increasingly sought after.
- Problem-Solving Abilities: The capacity to identify, analyze, and resolve issues efficiently is invaluable, especially in streamlining processes and enhancing product quality.
- Lean Manufacturing Principles: Knowledge of lean manufacturing techniques that minimize waste and maximize productivity is a plus.
- Digital Literacy: With the rise of Industry 4.0, being adept at using digital tools and understanding digital manufacturing processes is crucial.
- Communication Skills: Clear communication fosters effective collaboration among team members, which is crucial for meeting project deadlines and ensuring quality.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: The fast-paced nature of manufacturing means being open to change and quickly adapting to new methods, technologies, or roles is critical.
For those looking to forge a successful career in manufacturing, focusing on these areas can prepare you for the challenges and opportunities. Moreover, commitment to ongoing learning and development will ensure your skillset remains relevant and competitive in this ever-evolving industry.
Current & Future Manufacturing Jobs Outlook
The future is bright for those eyeing a career in manufacturing jobs. Entering the 21st century, the industry is on the brink of a tech revolution, indicating exciting opportunities and advancements.
- Technological Innovation: The adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT, AI, and advanced robotics, is set to transform manufacturing processes. Professionals skilled in these areas will be in high demand.
- Sustainability Focus: The drive towards green manufacturing and sustainability will create a surge in jobs focused on eco-friendly production techniques and energy efficiency.
- Global Market Influence: As global markets evolve, so will the demand for innovative products and efficient manufacturing processes. This global perspective opens up opportunities for professionals with an eye on international trends and market needs.
- Skilled Labor Shortage: The current gap in the skilled workforce – from machinists to manufacturing engineering jobs – presents an opportunity for new entrants and current professionals to advance their careers.
Despite challenges such as automation and offshore competition, the outlook for manufacturing jobs is positive, underscored by steady growth projections. Aspiring manufacturers succeed by adopting tech, lifelong learning, and supporting sustainable practices. Manufacturing’s future hinges on making processes brighter, cleaner, and more inclusive, not just output.
FAQ’s
What educational background do I need for a career in manufacturing?
While many positions start with a high school diploma or GED, advancing in the field often requires postsecondary education, technical certifications, or a degree in a related field like manufacturing engineering or industrial technology. Continuous learning and specialized certifications can significantly improve job prospects and advancement opportunities.
Which manufacturing skills are most in demand?
Technical skills in CNC machining, additive manufacturing, and robotics are highly sought after. Soft skills such as problem-solving, effective communication, and adaptability are equally essential to thrive in the fast-paced manufacturing environment.
How do technological advancements affect manufacturing careers?
Technological advancements, including automation and digital manufacturing, are reshaping the industry. They demand a workforce skilled in new technologies and open to continuous learning. While some fear technology may displace jobs, it also creates new roles requiring advanced skill sets.
Can manufacturing jobs offer a sustainable career path?
Absolutely. The manufacturing sector, vast and varied, spans from traditional machining to innovative roles in additive manufacturing and AI. With a focus on sustainability and innovation, the industry is set for long-term growth, providing a stable and rewarding career path for those ready to evolve with it.
Is there a demand for manufacturing professionals in the US?
There is a significant demand for manufacturing professionals in the US, driven by emerging technologies, reshoring efforts, and the ongoing need for skilled labor. The industry aims to fill the skills gap by attracting a diverse, new workforce ready for modern manufacturing’s challenges and opportunities.
Additional Resources
Numerous resources are available to explore the world of manufacturing further and hone your skills and knowledge. Here are some websites that can offer guidance, training, and insights:
- The National Institute of Standards and Technology Manufacturing Extension Partnership (NIST MEP) offers small and medium-sized manufacturers resources, including workshops, training, and innovation strategies to improve production processes.
- Advanced Manufacturing National Program Office (AMNPO) is dedicated to improving the competitiveness of U.S. manufacturing. It provides information on advanced manufacturing technologies, research and development, and industry partnerships.
- The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) provides resources for engineering professionals, including publications, conferences, and professional development opportunities in manufacturing and other fields.
- American Society for Engineering Education (ASEE) encourages innovation in education to prepare engineers to enter the global workforce, offering resources, professional development, and networking opportunities for educators and students alike.
- U.S. Department of Labor’s Apprenticeship program offers opportunities for hands-on training in various manufacturing trades, helping individuals earn. At the same time, they learn and build a solid foundation for a rewarding career.
These resources help those aiming to enhance their manufacturing knowledge, skillset, or career growth. By leveraging these opportunities, aspiring and current manufacturing professionals can stay at the forefront of industry trends and innovation.
Conclusion
The world of manufacturing jobs is one of dynamic change and immense opportunity. From the workshop floor to the heights of engineering innovation, manufacturing offers diverse pathways for career growth and fulfillment. Securing the right education, mastering sought-after skills, and keeping up with industry trends are crucial to success in this field. The future of manufacturing is not just about machines and materials but about the people who bring ideas to life.
We invite you to dive deeper into your manufacturing career journey by joining Diversity Employment. Creating an account and uploading your resume allows you to access a world of diverse staffing jobs that value inclusion, innovation, and your unique skill set. Be part of a community that champions inclusive growth and connects you with employers invested in creating diverse workplaces. Your next manufacturing dream job could be just a click away!




