Key Points
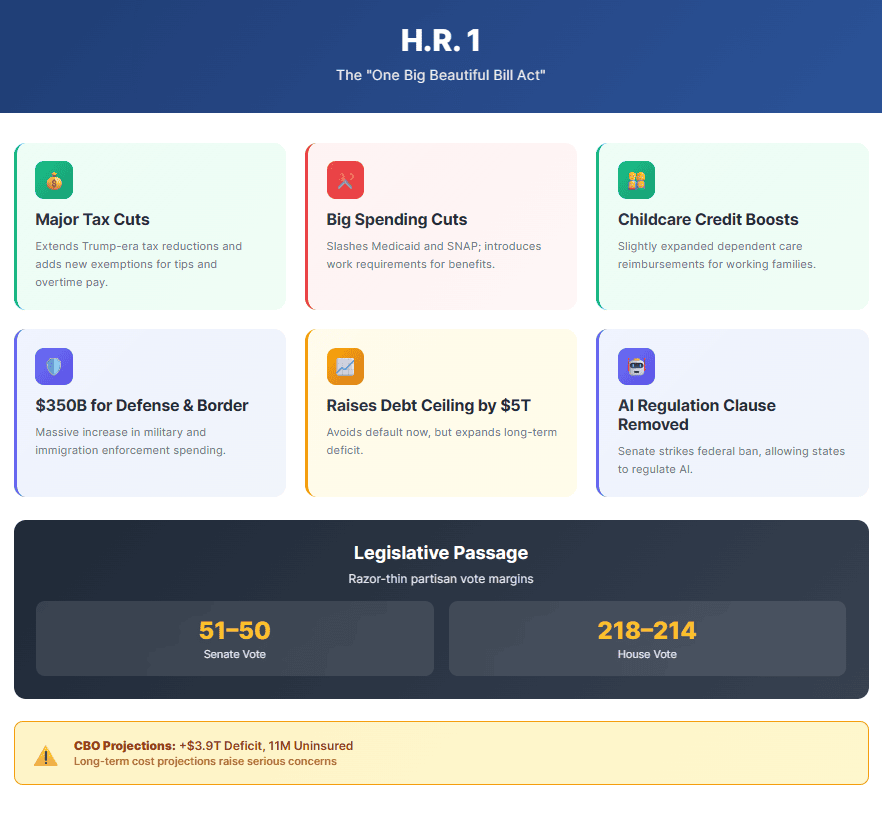
Image created by the Diversity Employment Team
Why This Bill Matters
H.R. 1, nicknamed the “One Big Beautiful Bill,” is the flagship legislation of the 119th Congress and a core part of President Trump’s legislative agenda. Spanning nearly 900 pages, it’s a sweeping proposal that touches nearly every corner of federal policy: tax cuts, healthcare, welfare, defense, immigration, AI regulation, and the national debt. With a razor-thin Senate vote and heated debates across both chambers, this bill isn’t just business as usual, it’s a high-stakes reshaping of domestic priorities.
Tax Spending Tradeoff: Cuts with Consequences
At the heart of the bill is a major extension of Trump-era tax cuts, including new breaks for tipped and overtime workers. While popular among working-class voters, these cuts come with a tradeoff: deep reductions to federal spending, especially in programs serving vulnerable populations. It’s a classic conservative approach, shrink government through reduced revenue and stricter eligibility requirements.
Example: A server in Florida making $2.13/hour in base pay and relying heavily on tips may now see more take-home pay due to tax exemptions on tips. But at the same time, a low-income family in Ohio may find it harder to qualify for food assistance due to stricter SNAP work requirements.
Potential upside: More money in pockets for certain types of workers, especially those in service industries.
Potential downside: Millions risk losing access to basic services if they don’t meet new eligibility criteria.
Program Changes: Medicaid, SNAP, and Childcare
Big cuts are coming to Medicaid and SNAP (food stamps), including the introduction of work requirements and tighter eligibility rules. States will also receive less generous federal reimbursements, prompting concerns about coverage loss. Meanwhile, there are modest expansions to childcare tax credits, like increased caps for dependent care reimbursements, but critics argue the benefits are dwarfed by the cuts elsewhere.
Example: A single mother in Arizona working part-time may now be disqualified from Medicaid if she can’t meet new work requirements, even though she’s actively job hunting. On the flip side, a dual-income family in Texas may now qualify for a larger childcare tax break, easing daycare costs.
Potential upside: Some middle-class families see real savings in childcare.
Potential downside: Vulnerable families could lose healthcare or food access entirely.
Defense & Border Spending: Security Takes Center Stage
Despite the cost-cutting elsewhere, defense and border security are big winners in this bill. Over $350 billion is set aside for military upgrades, missile defense, and new immigration enforcement efforts. The funding signals a clear pivot toward national defense and hardline border policy, aligning with Trump’s 2024 campaign promises.
Example: A military base in North Carolina may get funding for upgraded housing and training facilities. Meanwhile, increased border patrol spending could mean more detention centers opening near the U.S.–Mexico border.
Potential upside: Enhanced military readiness and improved quality of life for service members.
Potential downside: Civil rights groups warn of expanded detentions and family separations at the border.
Debt Ceiling Controversy: A $5 Trillion Leap
H.R. 1 raises the national debt ceiling by $5 trillion, which is an eye-popping increase that sparked major pushback from fiscal conservatives. House Republicans largely supported the move, framing it as necessary to avoid a government default, while critics argued that the paired tax cuts will only worsen the deficit problem they claim to solve.
Example: Federal workers and Social Security recipients avoid payment delays that would have occurred in a government shutdown. But economists project higher long-term borrowing costs due to expanded deficits.
Potential upside: Avoids immediate fiscal crisis.
Potential downside: Long-term risk of higher interest rates, inflationary pressure, and reduced fiscal flexibility.
AI Provision U‑Turn: Senate Strikes Controversial Rule
An earlier version of the bill included a 10-year federal ban on states passing their own AI regulations. That provision was ultimately removed in the Senate, following backlash from both Democrats and Republicans concerned about stifling state innovation or oversight. It’s one of the rare bipartisan reversals in an otherwise partisan bill.
Example: California is now free to implement its planned AI safety laws, including transparency rules for hiring algorithms, something the House version would have blocked.
Potential upside: States retain flexibility to innovate and protect consumers.
Potential downside: Businesses face patchwork regulation, increasing compliance complexity.
Political Backlash & Support: A Party Tug-of-War
The bill passed the Senate 51–50, with Vice President J.D. Vance casting the tie-breaking vote. Along the way, several Republicans, including Senators Rand Paul, Lisa Murkowski, and Susan Collins, voiced serious concerns over healthcare cuts and deficit growth. Meanwhile, Democrats mounted a record-setting amendment campaign to delay or soften the bill, but very few changes made it through.
Example: Murkowski held up final approval to secure rural healthcare protections in Alaska. Meanwhile, progressives tried but failed to restore green energy tax credits.
Potential upside: Legislative horse-trading secured minor concessions in key swing states.
Potential downside: Most opposition was overridden, and the final bill passed with minimal changes.
CBO Cost Projections: Billions Slashed, Trillions Added
The Congressional Budget Office estimates that the bill will add around $3.3 trillion to the deficit over the next decade, with interest pushing that figure closer to $3.9 trillion. It also forecasts that over 11 million Americans could lose health coverage due to the Medicaid reforms. Supporters argue this is a necessary correction to government overreach; critics say it’s fiscal recklessness dressed as reform.
Example: A diabetic senior in West Virginia might lose access to Medicaid-funded insulin due to the reimbursement cuts, while high earners in Florida benefit from permanent tax breaks.
Potential upside: Tax relief may stimulate short-term economic growth.
Potential downside: Massive uninsured population and ballooning deficit could hurt long-term stability.
Next Step: Presidential Signature
Following Senate approval, the House officially passed the revised version of H.R. 1 in a narrow 218–214 vote on July 3, 2025. With both chambers now in agreement, the bill heads to the President’s desk for a signature.
H.R. 1 is set to define the legislative direction of the next two years. Whether it’s a bold vision or a dangerous gamble depends on your perspective. Either way it is, undeniably, a BIG pivot point moment in U.S. policy.




